What is Google Scholar? Features, History, and How It Works
What is Google Scholar? 🎓
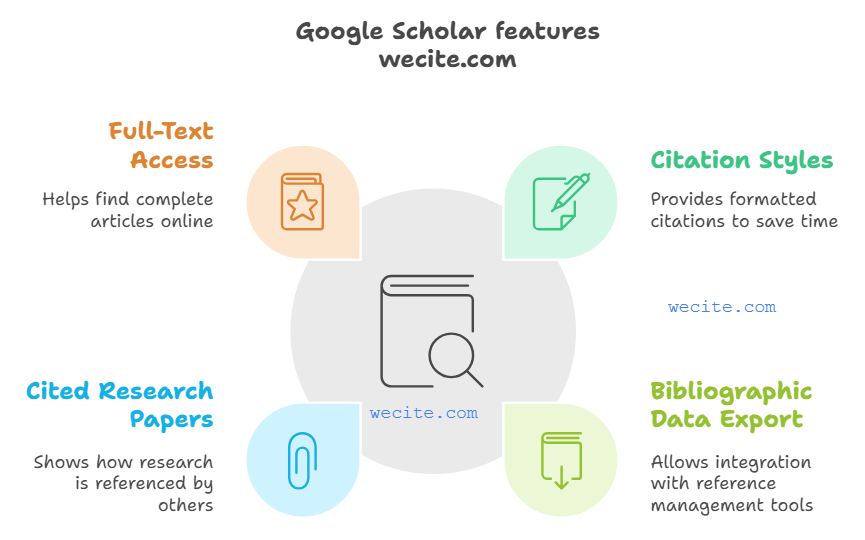
Google Scholar is like the academic version of Google, designed for students, researchers, and anyone who needs to find scientific literature. It searches through a ton of sources at once, like:
- Articles 📑
- Books 📚
- Theses
- Court opinions ⚖
- Content from academic publishers and societies
If you’re looking for something scholarly, Google Scholar’s got your back, making it easy to quickly find specific papers or do a quick search on a topic.
How Google Scholar is Different from Regular Google
Unlike your regular Google search that pulls up everything from blogs to shopping sites 🛒, Google Scholar is all about scholarly literature. This makes it a great tool for research because it cuts out all the junk and focuses only on the academic stuff.
However:
- It’s not the best for getting a full picture of a topic, like when you’re writing a thesis or doing a literature review.
- The search options are kind of limited, especially when combining terms with AND, OR, and NOT.
- It defaults to searching the full text of articles, and while you can filter by things like title, author, or date, it doesn’t let you zero in on just titles, abstracts, or keywords like some other databases do.
Origins of Google Scholar
Google Scholar was started by Alex Verstak and Anurag Acharya, who were working on building Google’s main web index. They wanted to help researchers and students find scientific knowledge easily. The whole idea was to make problem-solving faster and more efficient. The slogan, “Stand on the shoulders of giants,” reflects this, highlighting the idea of building on past knowledge—a nod to Isaac Newton’s famous quote. A big chunk of its content comes from the University of Michigan’s print collection, adding tons of academic sources to the mix.
Evolution and Features of Google Scholar
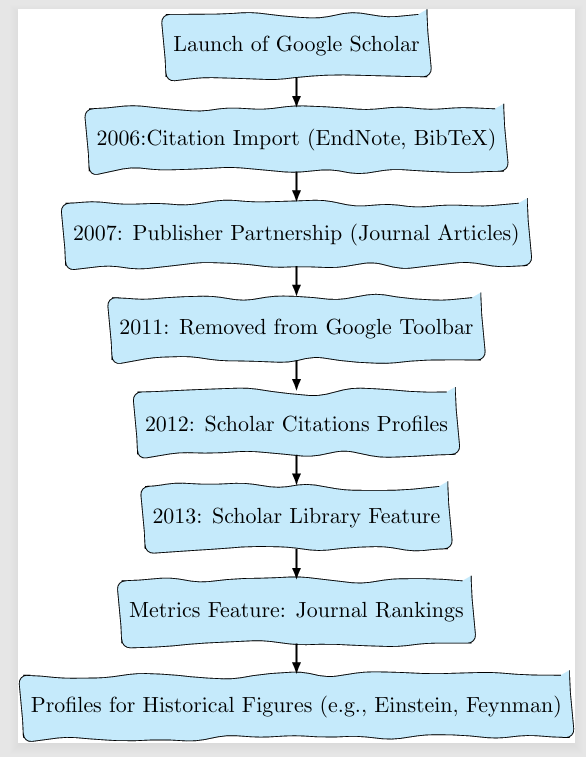
Over the years, Google Scholar has rolled out a bunch of new features:
- In 2006, they added the ability to import citations into tools like EndNote and BibTeX, making it easier to manage references.
- In 2007, they partnered with publishers to digitize and host journal articles directly, which was separate from Google Books.
- Although Scholar was removed from the Google toolbar in 2011, it still kept growing.
Recent Additions and Updates
In 2012, they launched Scholar Citations profiles, allowing researchers to create personal profiles and track their publications.
- The Scholar Library feature came out in 2013, letting users save and organize articles.
- There’s also a metrics feature to see which journals are leading in different fields and check the impact of articles.
- They even created profiles for historical figures like Albert Einstein and Richard Feynman.